Connecting telematics technology to your vehicle
Understanding the onboard diagnostics in the vehicle is important. Connecting to your Vehicle with the Diagnostic link connector

The DLC (diagnostic link connector) is the physical and electrical connection to the vehicle. Not only does it give a location to mount the device, but also it supplies the power and the protocol interface to the ECU (Electronic Control Unit). This connection is the port to the vehicle data, and it is critical that all installations are secure and that proper hardware is used.
A great deal of engineering time has gone into making the Geotab GO device easy to install. With that said, much engineering time has also been put into investigating issues in the field that are mainly caused by improper installations. Utilizing the tools and the hardware to provide a secure connection and getting device confirmation is the key to insuring a successful installation and data set. We all know revisiting the vehicle at a later date is a costly venture and inconvenient for all parties involved.
Understanding the onboard diagnostics in the vehicle can shed some light on the importance on a good install.
Since 1996, this J1962 connector has been used and provide a connection for diagnostic tools for OBD II and manufacturers discretion data.
Read more about the interesting history of OBD II in this post.
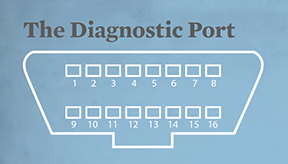
2. Bus positive Line of SAE-J1850 PWM and SAE-1850 VPW
4. Chassis ground
5. Signal ground
6. CAN high (ISO 15765-4 and SAE-J2284)
7. K line of ISO 9141-2 and ISO 14230-4
10. Bus negative Line of SAE-J1850 PWM only
14. CAN low (ISO 15765-4 and SAE-J2284)
15. L line of ISO 9141-2 and ISO 14230-4
16. Battery voltage
1, 3, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13. Manufacture discretion
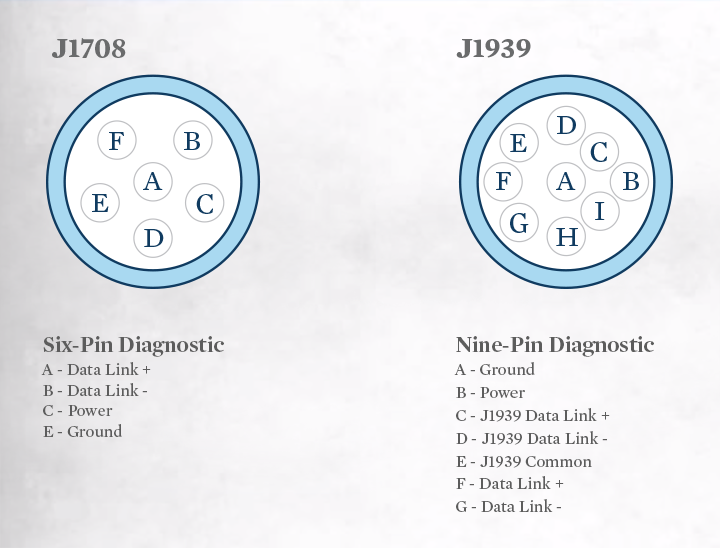
Vehicle diagnostics is available through various protocols. This information delivers a wealth of information on the workings and metered data within the network. As with any network device when plugged in, it becomes a electrical node and its properties can affect the behaviour of the other nodes on the same connection. Some protocols such as the J1850VPW, J1939, J1587 and ISO15765 on the diagnostic connector may have critical data and are needed for operational purposes, and a bad connection on a device anywhere on the network can cause issues.
Field visits to vehicles have uncovered many connection issues - whether they are wrong harness being used or not pushed in all they way, tie strapped, or locked. This type of problem may only show itself at a later time when vehicle is in service due to vibrations or involuntary kicking of device. It is important to make sure the install is done right the first time.
For any Geotab GO device installation related questions, please reach out to your Authorized Geotab Reseller.
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
Tom Walli is a Senior Automotive Specialist for Geotab.
Table of Contents
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
Related posts

What is government fleet management software and how is it used?
April 10, 2025
3 minute read


Geotab: Unlocking value and enhancing K-12 transportation with data-driven fleet management
February 21, 2025
1 minute read

Driver incentive programs to improve safety, retention and fleet efficiency
February 7, 2025
4 minute read
.jpg)
School bus fleet management 101: A comprehensive guide
February 5, 2025
4 minute read
