What is last-mile delivery? (Cost + benefits guide)
Discover how last-mile delivery impacts costs, efficiency and customer satisfaction, and learn how technology can help streamline the process.


Key Insights
- Last-mile delivery is the final step in transporting goods from a distribution hub to the customer’s doorstep.
- The process can be costly due to factors like fuel, labor and complex routes.
- Efficient fleet management and route optimization are key to improving last-mile delivery efficiency and profitability.
As e-commerce continues to boom, efficient last-mile delivery has become a competitive necessity for businesses across industries. It’s the final step in the shipping process, where goods travel from a transportation hub to their final destination.
With a global freight trucking market valued at $2.2 trillion and over 3.54 million truck drivers in the U.S. alone, the scale of last-mile logistics is enormous. However, challenges like rising costs, delivery inefficiencies and environmental concerns are pushing companies to innovate.
Learn how last-mile delivery works, how much it costs and what innovative technologies are transforming it.
What is last-mile delivery?
Last-mile delivery is the final leg of the delivery process, where goods are transported from a local distribution center to their ultimate destination — typically a customer’s home or business.
This stage is often the most complex and costly part of the supply chain, as it involves navigating local roads and meeting customer expectations for speed and accuracy.
For businesses with a last-mile delivery fleet, this process is critical to ensuring customer satisfaction and maintaining efficient operations. Companies in e-commerce, retail and food delivery are most affected by last-mile logistics, but they mostly use a vehicle tracking device to improve route planning and reduce delays.
How does last-mile delivery work?
The last-mile delivery process involves several key stages that ensure drivers efficiently transport goods from a distribution center to their final destination. From order placement to the final handoff, coordination between various teams, vehicles and technologies is a must for success. Here’s how it works.
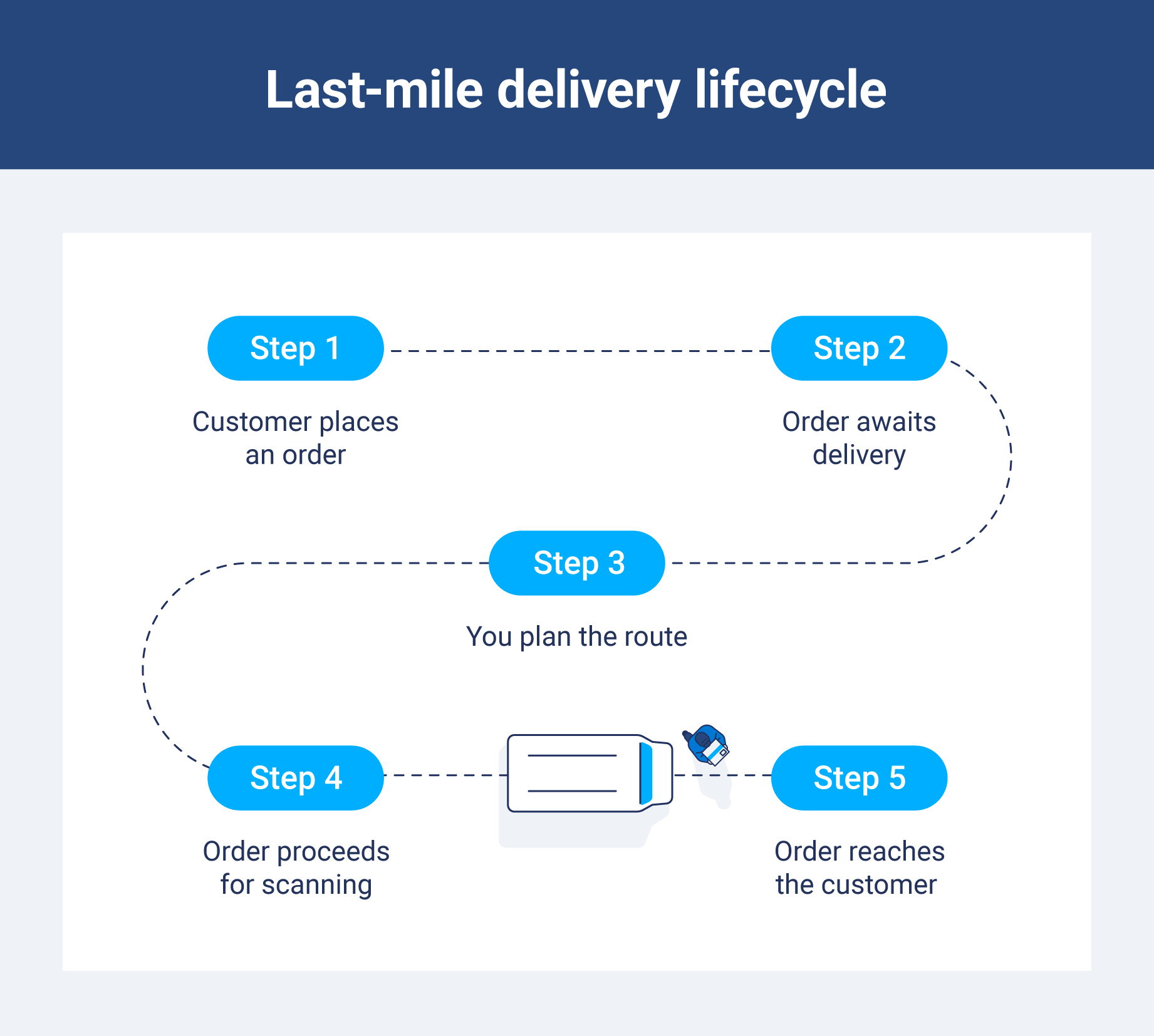
Step 1: Customer places an order
The journey begins when a customer places an order, whether online or through a mobile app. The request is logged, and the item is prepared for shipment. This stage marks the start of the delivery process, where the system gathers the necessary information, such as product availability and customer location, to begin processing the delivery.
Step 2: Order awaits delivery
Once the order is ready, it is transported to a last-mile sorting and distribution center. Here, orders are organized and prepared for the final leg of their journey. Depending on the delivery method and destination, orders are sorted according to their location, waiting for the next available delivery vehicle.
Step 3: You plan the route
Once the order reaches the distribution center, a route planner assigns it to a last-mile delivery vehicle. Rethinking delivery routes is essential to the process, as optimized routes help reduce delivery time and cost. The system may also assign a driver and equip them with the tools needed for the delivery.
Step 4: Order proceeds for scanning
Before the delivery begins, the order is scanned, and tracking information is updated. Customers typically receive real-time notifications on their order status, allowing them to track the shipment from the distribution center to their doorstep. This stage ensures that customers are informed and that any issues along the way can be quickly addressed.
Step 5: Order reaches the customer
In the final step, the order is delivered to the customer. The last-mile delivery vehicle navigates to the customer’s address, and the package is handed off — often requiring a signature or a photo to confirm delivery.
With the rise of same-day and next-day deliveries, this stage has become vital to customer satisfaction, making efficient, timely service crucial for businesses to maintain a competitive edge.
Common last-mile delivery challenges
Last-mile delivery is key to customer satisfaction, but several challenges can impact its efficiency and increase costs. From expensive operational needs to logistical hurdles, you must address these issues to streamline your delivery process and improve service quality.
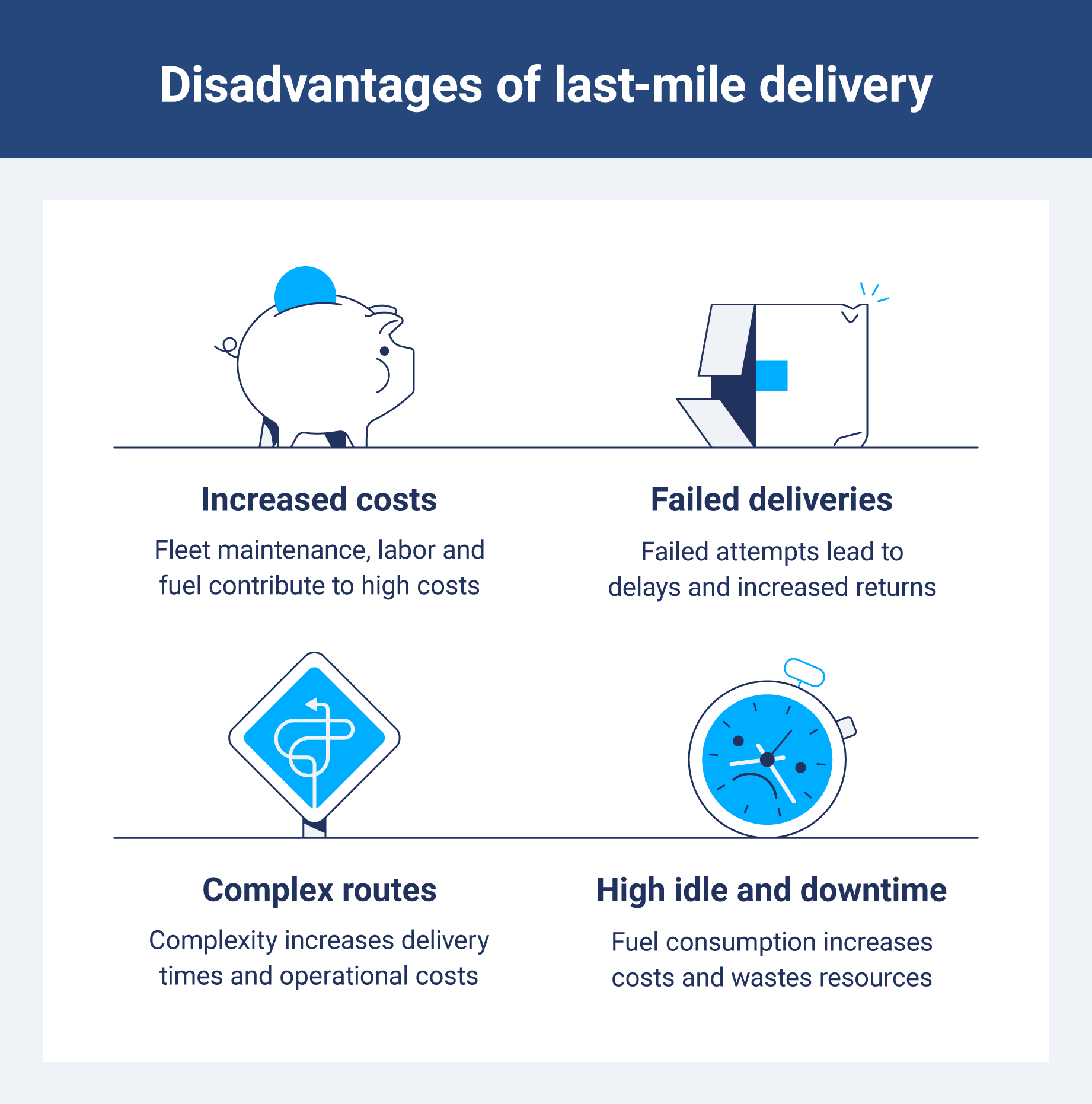
Increased costs
Factors like labor, fuel and fleet maintenance contribute significantly to last-mile delivery costs. With the rise in demand for faster deliveries, these costs continue to climb. Vehicle maintenance, for example, can lead to higher expenses, especially if the fleet is aging or if unforeseen breakdowns occur.
Example: As a fleet of delivery vehicles ages, it may require more frequent maintenance, resulting in rising costs for repairs and replacements. These additional expenses are passed on to the customer or absorbed by the business, affecting the overall delivery budget.
Failed deliveries
When customers are unavailable to receive their packages, failed deliveries can occur, leading to delays and the need for additional delivery attempts. This adds extra labor costs and can lower customer satisfaction as the delivery window expands. Sometimes, failed attempts can result in returns or missed business opportunities.
Example: A delivery attempt was made, but the customer wasn’t home to receive the package, causing a delay of several days as the second attempt was rescheduled.
Complex routes
Delivering to rural or remote areas presents its own set of challenges. The lack of infrastructure and longer distances can increase delivery times and operational costs in these regions.
Navigating difficult terrain or low-density areas often results in higher fuel consumption and longer travel times, making meeting customer expectations for fast deliveries more difficult.
Example: A delivery to a rural area involved longer travel time and higher fuel consumption due to limited access roads and less efficient route planning, which increased the business's costs.
High idle and downtime
Traffic congestion, poorly planned routes or waiting for customers can lead to extended periods of idle time for delivery vehicles. This not only increases fuel consumption but also wastes valuable resources, as vehicles remain stuck or waiting for long stretches. High idle times also contribute to vehicle wear and tear, further increasing fleet maintenance costs.
Example: Delivery trucks spent hours stuck in heavy traffic, leading to increased fuel consumption and wasted time that could have been spent on completing additional deliveries. Poorly planned routes added to the inefficiencies.
Last-mile delivery cost breakdown
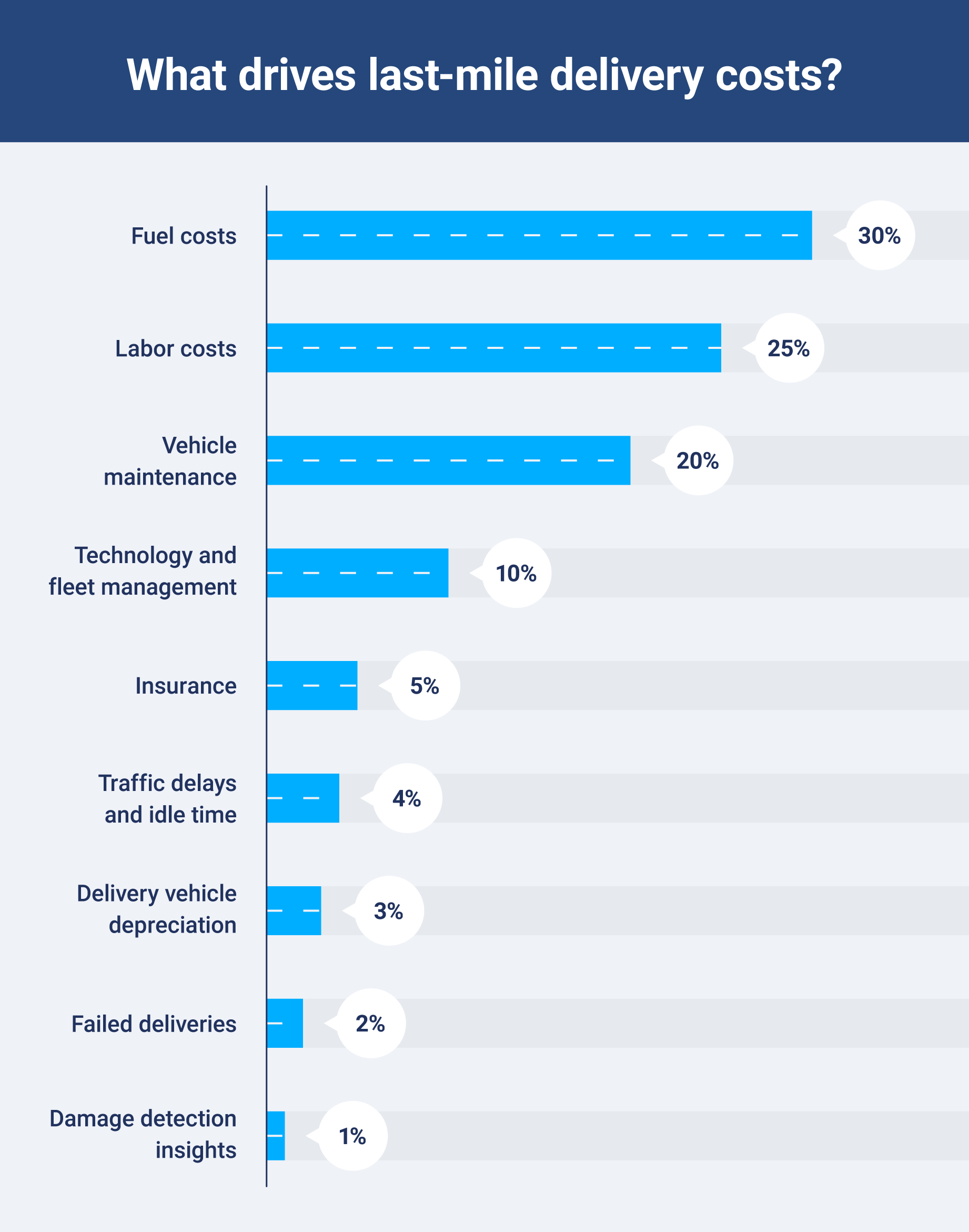
Last-mile delivery costs can quickly add up due to various factors contributing to operational expenses. From fuel and vehicle maintenance to labor and technology costs, understanding what drives these expenses is essential for businesses aiming to optimize their delivery process.
Here are the main costs that impact the operation of last-mile delivery fleets:
- Fuel costs (30%): Fuel is a major expense for any delivery fleet, with fuel prices fluctuating based on geography and demand.
- Vehicle maintenance (20%): Regular maintenance, including repairs, tire replacement and general upkeep, contributes to long-term fleet costs.
- Labor costs (25%): Delivery driver wages, benefits and other compensation make up a significant portion of last-mile delivery expenses.
- Technology and fleet management (10%): Software for tracking, route planning and optimizing deliveries adds to the operational cost, but also helps reduce inefficiencies.
- Insurance (5%): Fleet and cargo insurance are essential for protecting goods and vehicles in transit, adding to the total cost of delivery.
- Delivery vehicle depreciation (3%): The aging of delivery vehicles impacts their value, and businesses must account for the depreciation as part of their operational budget.
- Traffic delays and idle time (4%): Vehicles stuck in traffic or delayed due to inefficiencies result in increased fuel use and vehicle wear and tear.
- Failed deliveries (2%): Additional costs accrue when deliveries fail, requiring extra attempts or returns.
- Damage detection insights (1%): Damage to goods during transit leads to additional costs for replacements, handling and potential customer dissatisfaction.
How technology solves the “last-mile problem”
Fleet management solutions, including route optimization software and advanced data storage systems, can help overcome last-mile delivery challenges. Integrating technology into the delivery process can streamline operations, reduce costs and improve overall efficiency. Here are more details:
- More efficient route optimization: Route optimization software helps determine the fastest, most cost-effective routes, reducing delivery time and fuel consumption.
- Improved driver safety: Fleet management systems monitor driver behavior, alerting managers to unsafe driving practices and ensuring safety measures are followed.
- Easier electrification: EV fleet management software simplifies the transition to electric vehicles by tracking energy usage, charging needs and fleet performance.
- Advanced analytics: Technology provides deep insights into operational performance, helping you make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency and profitability.
- Increased customer satisfaction: Real-time tracking and communication tools ensure customers receive up-to-date delivery information, enhancing their overall experience and satisfaction.
- Reduce maintenance costs: Predictive maintenance tools analyze vehicle data to identify potential issues before they occur, reducing downtime and repair costs.
Streamline last-mile delivery with fleet optimization software
Fleet optimization software helps you improve efficiency by optimizing routes, reducing fuel consumption and increasing overall fleet performance. As fleets consider electrification, Geotab’s EV Suitability Assessment (EVSA) tool helps identify vehicles suitable for EV adoption, offering savings and sustainability benefits.
Also, with the growth of last-mile delivery expectations, courier fleets face greater pressure to stay efficient and meet customer expectations. Use fleet management and optimization software to improve route efficiency, reduce costs and keep your fleet running smoothly.
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
Frequently Asked Questions
Last-mile delivery refers to the final step in the delivery process, where goods are transported from a distribution hub to the customer’s doorstep.
Last-mile logistics involves the planning, transporting and managing of goods from the final distribution point to the customer, focusing on efficiency and timely delivery.
The “last-mile problem” refers to the challenges of efficiently delivering goods in the final leg of the delivery process, which is often impacted by traffic, route optimization and customer availability.
Last-mile delivery is costly due to factors like high fuel consumption, labor expenses, vehicle maintenance and the complexity of navigating urban areas or remote locations.
Last-mile delivery can be profitable when managed efficiently, but high operational costs often make it challenging. Effective fleet management and route optimization help increase profitability.

Corinda Ouellet is a Marketing Manager, Segment at Geotab.
Table of Contents
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
Related posts


How to avoid high downtime costs for construction fleets
March 10, 2025
2 minute read

Empowering Choice: The Power of Collaboration in Our Marketplace
January 15, 2025
1 minute read

Top 7 Transportation Management Systems (TMS) Software
December 5, 2024
7 minute read

What is route optimization? A guide to improving fleet efficiency
December 4, 2024
4 minute read

Developing a next-gen government fleet safety program: Made possible with AI
November 26, 2024
2 minute read