What Is Fleet Management? A Complete Guide for Fleet Managers
Discover how fleet management can streamline your operations and boost your bottom line.

Key Insights
- Fleet management is the process of overseeing and optimizing a fleet of vehicles.
- Fleet managers oversee all aspects of fleet management and handle tasks like vehicle maintenance, driver management, fuel optimization and compliance.
From vehicle acquisition and maintenance to driver management and fuel efficiency, a fleet manager performs many important tasks. But what does fleet management entail?
An effective fleet management strategy will reduce fuel costs, improve vehicle uptime, enhance driver safety and increase operational efficiency.
Let’s dive into the fleet management process and how implementing a fleet management system can help streamline operations when managing EVs and gas-powered vehicles.
What is fleet management?
Fleet management is the process of overseeing and optimizing a fleet of vehicles. It involves a range of activities, from vehicle acquisition and maintenance to driver management and fuel efficiency.
The activity of fleet management can drive valuable benefits like increasing vehicle acquisition efficiency, fuel management, fleet compliance, increasing driver safety and reducing carbon emissions.
Why fleet management is important
Whether one truck or 10,000 trucks, fleet management is critical to the success of business operations. Tracking the location and condition of vehicles, as well as maintenance schedules and fuel consumption, aids in fleet cost management and extends the life of equipment.
The overall purpose of fleet management is continual improvement. Within this, there are many goals, including:
- Tracking vehicles and equipment
- Increasing safety
- Monitoring the vehicle lifecycle
- Boosting efficiency
- Enhancing productivity
- Maintaining fleet compliance
As more companies embrace electric vehicles and fleet sustainability, lowering emissions is also a key goal.
How does fleet management work?
Fleet management fundamentally works the same across any business that leases or owns a fleet of vehicles. The process and strategy of fleet management is to maintain smooth and efficient operations and involve the following core strategies:
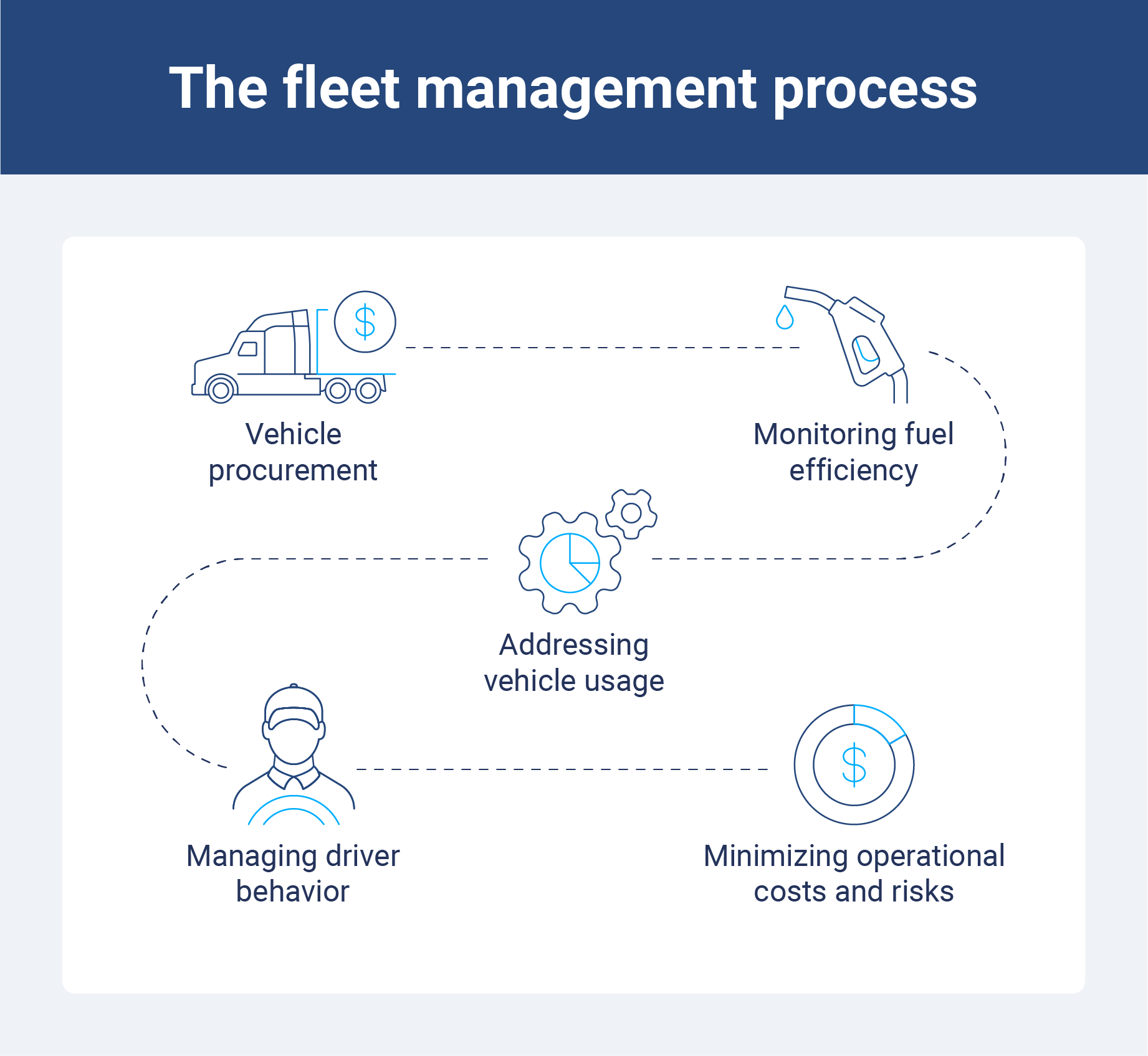
- Vehicle procurement: This is the process of organizing fleet assets through purchasing or leasing to meet a fleet’s specific needs. Fleet managers need to create procurement plans that align with their current fleet operations and overall company goals.
- Monitoring fuel efficiency: Fuel is often one of the largest costs for fleets, which is why proper management of fleet fuel cards is key. To manage fuel efficiency and reduce costs, fleets need to track vehicle idling, speeding, tire pressure, routing and vehicle size, weight and type.
- Addressing vehicle usage: This is the process of understanding where your fleet vehicles are, what they are doing, who is driving them, when they are in use, why they are being used and how to better manage their operations.
- Managing driver behavior: Fleet operations can only be successful if drivers are on board with the rules outlined by your organization. By engaging drivers through coaching, incentives, performance metrics and feedback, your fleet can become more productive.
- Minimizing operational costs and risks: From collisions to overhead costs, compliance fines to excessive fuel consumption, all fleets should assess their highest operational costs and work to reduce them with fleet management procedures.
There is constant pressure to reduce the total cost of ownership, enforce fleet safety policies, minimize risk and increase productivity. Because of this, fleet managers use telematics technology, data analytics and software that can help them confront the many business challenges they face.
What does a fleet manager do?
Fleet managers are responsible for overseeing and managing an organization's fleet of vehicles. This role involves a wide range of duties, from ensuring driver safety and compliance to optimizing vehicle maintenance and fuel consumption.
1. Driver training and compliance
Fleet managers oversee driver training programs to ensure compliance with safety regulations and company policies. This includes:
- Conducting regular driver training sessions
- Reviewing driver licenses and certifications
- Maintaining accurate driver records
- Monitoring driver behavior and performance
- Ensuring compliance with local, state and federal regulations
2. Fleet maintenance
Fleet maintenance is the management of policies and processes designed to keep company vehicles in safe and reliable operating conditions to protect drivers and residual value. Fleet managers are responsible for:
- Developing and implementing vehicle maintenance schedules
- Overseeing vehicle inspections and repairs
- Managing parts and inventory
- Tracking vehicle performance and identifying potential issues
- Minimizing downtime and maximizing vehicle lifespan
3. Contract management and fiscal planning
Fleet managers play a key role in managing the financial aspects of fleet operations, including:
- Negotiating contracts for vehicle purchases and leases
- Developing vehicle replacement plans
- Managing fuel and maintenance contracts
- Monitoring fleet costs and identifying opportunities for savings
- Disposing of old or damaged vehicles
4. Fuel management
Fuel management is a significant cost factor for fleets. Fleet managers are responsible for managing fuel types, including:
- Gasoline
- Natural gas
- Electric energy
This also includes the repair and related compliance procedures associated with fuel needs.
5. Route planning and optimization
Efficient route planning is essential for maximizing productivity and minimizing costs. Fleet managers use advanced routing software to:
- Optimize delivery routes and schedules
- Assign the right vehicles to the right jobs
- Monitor real-time vehicle locations and traffic conditions
- Reduce fuel consumption and minimize driver fatigue
- Improve customer satisfaction through timely deliveries
Challenges fleet managers face
Fleet management can be a complex task, and managers often face a variety of challenges.
Route optimization
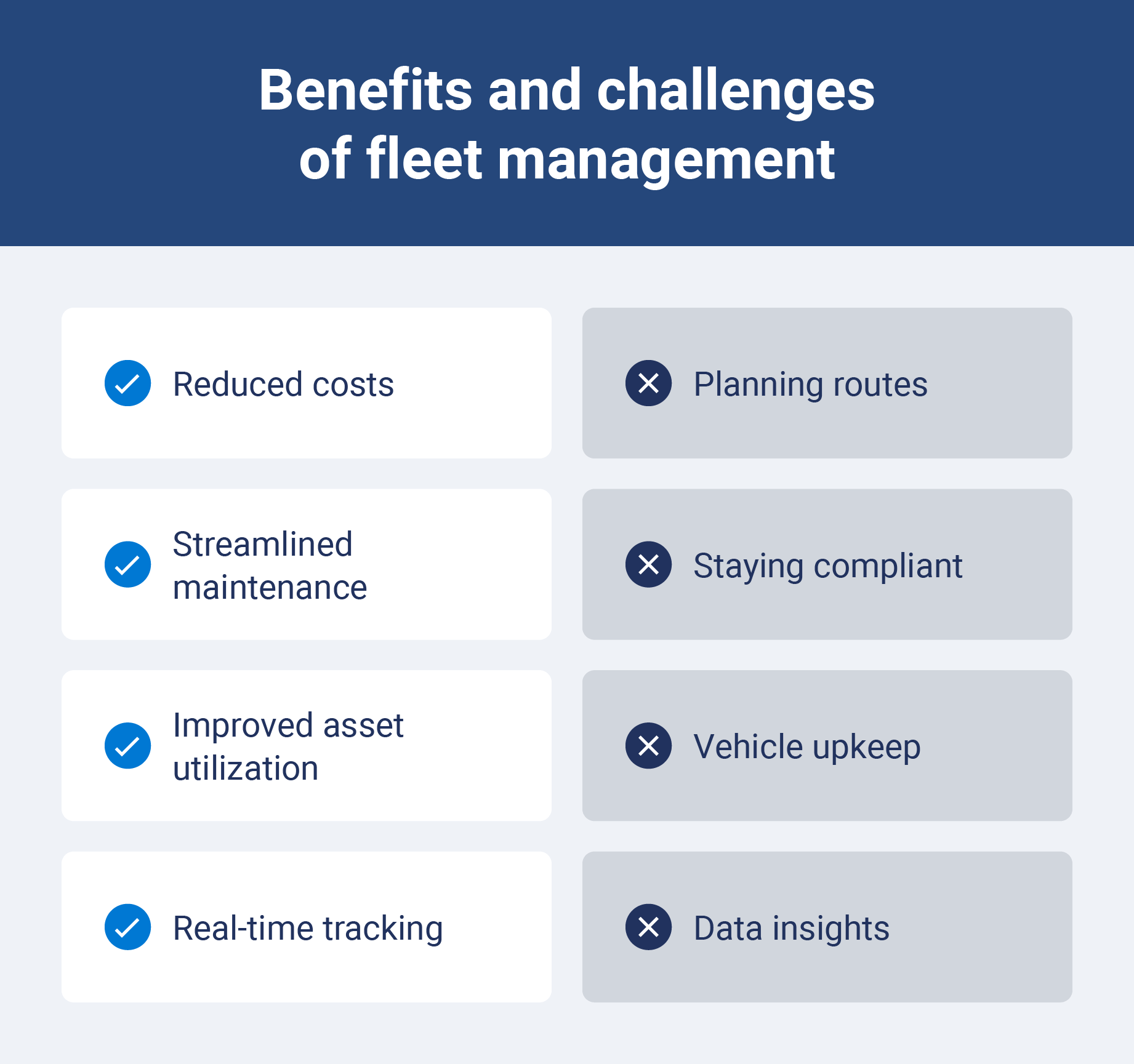
Route optimization is a critical aspect of fleet management. Poorly planned routes can lead to increased fuel consumption, longer travel times and driver fatigue. Traffic congestion and dynamic factors like collisions and weather can further complicate route optimization efforts.
Compliance & regulations
Compliance and regulations are another significant challenge. Fleet managers must ensure that their vehicles and drivers adhere to all relevant regulations, including DOT regulations, emissions standards and safety standards.
Additionally, managing driver hours of service (HOS) to prevent drowsy driving-related incidents is crucial. Regular vehicle inspections and maintenance are essential to ensure safety and compliance.
Vehicle upkeep
Vehicle upkeep is a continuous challenge. Preventive maintenance is crucial to prevent breakdowns and extend the life of vehicles. However, unexpected breakdowns and repairs can disrupt operations and increase costs. Protecting vehicles from theft and vandalism can also be a concern for fleet managers.
Data insights
Data insights play a vital role in effective fleet management. Gathering and analyzing data from various sources, such as vehicle tracking devices and telematics systems, can help identify trends, patterns and areas for improvement. By leveraging data-driven insights, fleet managers can make informed decisions about vehicle procurement, maintenance and routing.
The role of telematics in fleet management
Telematics is commonly integrated into fleets via vehicle on-board diagnostic (OBD) ports to provide data into software platforms. Telematics can be used to encourage safer, more eco-friendly driver behavior and influence compliance with fleet policies. In addition, telematics can:
- Improve customer service through the use of real-time GPS monitoring, trip reporting and dispatching and routing
- Provide in-car driver coaching, risk and driver behavior reporting, crash notifications, reconstruction and location tracking for missing or stolen vehicles or equipment
- Use predictive maintenance and remote diagnostics to streamline maintenance and remote diagnostics
- Perform fuel management by monitoring idling and other driving habits
- Simplify fleet compliance with easy tools for electronic logging, Hours of Service (HOS) and driver vehicle inspection reporting (DVIR)
- Integrate with other software systems, such as onboard camera technology or CRM software and even create new applications
- Manage electric vehicles (EVs) while reducing a fleet's environmental impact and carbon emissions
Benefits of using a fleet management system
Fleet management software (FMS) is a computer or cloud-based software that allows a person or team to manage tasks associated with managing fleet vehicles. These specific tasks cover everything from vehicle procurement to vehicle disposal.
Reduced costs
Fleet management software can help you reduce costs in a variety of ways, including:
- Lower fuel costs: Optimizing routes and identifying fuel-efficient driving habits can significantly reduce your fuel expenses.
- Reduced maintenance costs: Tracking vehicle maintenance schedules and identifying potential issues early on can help prevent costly breakdowns and repairs.
Streamlined maintenance
With automated reminders, FMS can help you streamline your maintenance processes by:
- Scheduling maintenance: Automatically schedule maintenance tasks based on vehicle usage and manufacturer recommendations.
- Tracking maintenance history: Keep track of all maintenance records, including repairs, inspections and oil changes.
- Generating maintenance reports: Generate detailed reports on maintenance costs, vehicle downtime and other key metrics.
Improved asset utilization
FMS can help you improve your fleet's utilization by:
- Tracking vehicle location: Monitor the location of your vehicles in real time to ensure drivers are using them efficiently.
- Identifying idle time: Identify vehicles that are not being used and redeploy them to more productive tasks.
- Optimizing routes: Plan efficient routes to minimize travel time and fuel consumption.
Real-time tracking & data
FMS can provide you with real-time vehicle data on your fleet, including:
- Vehicle location: Track the location of your vehicles in real time.
- Vehicle speed: Monitor the speed of your vehicles to identify potential speeding violations.
- Engine hours: Track the engine hours of your vehicles to schedule maintenance and repairs.
- Fuel consumption: Monitor fuel consumption to identify potential fuel theft or inefficient driving habits.
- Driver behavior: Track driver behavior, such as hard braking, excessive acceleration and speeding.
Streamline fleet management with the right software solution
Fleet management software can improve your business operations by providing real-time insights into your fleet's performance. With features like GPS tracking, vehicle diagnostics and driver behavior monitoring, you can optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption and enhance safety.
Ready to take control of your fleet? Explore our fleet management solutions or learn more about what fleet management is.
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
Frequently Asked Questions
A fleet manager oversees a company's fleet of vehicles, ensuring their efficient and safe operation. They handle tasks like vehicle maintenance, driver management, fuel optimization and compliance.
Fleet services refer to the management, maintenance and operation of a company's fleet of vehicles. This includes tasks like vehicle maintenance, driver management and fuel optimization.
A fleet management system (FMS) is a software solution that helps businesses manage their fleet of vehicles efficiently. It tracks vehicle location, fuel consumption, maintenance schedules and driver behavior to improve operational efficiency and reduce costs.
For example, a delivery company with a fleet of trucks uses a fleet management system to track vehicles in real time, schedule maintenance and optimize routes to save fuel.
The Geotab Team write about company news.
Table of Contents
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
Related posts

How to avoid high downtime costs for construction fleets
March 10, 2025
2 minute read

Geotab: Unlocking value and enhancing K-12 transportation with data-driven fleet management
February 21, 2025
1 minute read


CSA scores: What they are and how to check and improve them
December 3, 2024
5 minute read

35+ drowsy driving statistics and prevention facts for 2024
November 15, 2024
5 minute read
