How telematics insights can help reduce your fleet’s scope 1 carbon emissions
With the surge in pressure for organisations to measure and reduce their carbon footprint, understand how to gain oversight of your fleet’s scope 1 emissions, and how connected vehicle insights will help you to reduce them.


Scope 1 carbon emissions
The GHG Corporate Protocol, the most recognised standard for measuring corporate greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, breaks the organisational carbon footprint into three ‘scopes’. Scope 1 emissions are categorised as those which are directly related to your own business activity. This includes the emissions produced from company-owned and controlled resources, including the fuel used in company vehicles.
Scope 1 emissions are those that organisations have the greatest control over, and therefore they are where many businesses look to start their decarbonisation journey.
The relevance of fleets for scope 1 emissions reporting
Fleets commonly represent one of the greatest sources of scope 1 emissions for an organisation. Fleet managers can therefore find themselves under considerable pressure to firstly measure, and then to reduce their GHG emissions.
Within the GHG Protocol Corporate Standard, fleets fall under the category of "mobile combustion emissions". This encompasses all emissions that come from owned or leased, and on-road or off-road vehicles that generate GHG emissions through the combustion of various fuels.
Fleet emissions include those from:
- On-road company vehicles
- Forklift trucks and other off-road vehicles
- Construction equipment
It can include the consumption of any of the following fuels:
- Petrol
- Diesel
- Biodiesel
- LPG, or propane gas
GHG emissions from fleet vehicles can be calculated by collecting data on the amount of fuel consumed, the distance travelled and the fuel characteristics for each vehicle. A fleet telematics system provides this data, alongside visibility into trends on fuel usage and fill-ups. Some can even integrate your fuel cards so that no fuel usage goes un-monitored.
Fleet strategies to reduce scope 1 emissions
Broadly, fleet sustainability strategies fall into three categories.
- Doing more with less; rightsizing the fleet to the real needs of the operation, and identifying opportunities to increase the utilisation of current vehicles and site equipment.
- Increasing the efficiency of operations; minimising transport mileage and improving the fuel efficiency of the vehicles within the existing fleet.
- Transitioning to more efficient vehicles; shifting the fleet towards alternative fuel vehicles that are scope 1 carbon neutral.
How Geotab’s features support your fleet sustainability strategies
Doing more with less
Geotab’s asset utilisation solutions provide real-time asset tracking for both on and off-road fleet vehicles, allowing you to track true asset utilisation and dwell time trends and identify opportunities to increase utilisation rates. This can ultimately result in the ability to downsize the fleet by eliminating under-utilised vehicles and site equipment.
With Geotab Keyless technology, organisations can provide a pool of vehicles to their employees rather than one for each employee in turn. This enables fleet managers to do more, without adding resources. Vehicle utilisation can be significantly improved, increasing efficiency and lowering operating costs by right-sizing the fleet to your real transport requirements.
Increasing the efficiency of operations
Geotab’s route optimisation partnerships enable dispatch teams to automatically optimise routes to increase efficiency, improving fuel economy and saving time. With real-time dispatching, you can send the best-suited driver to any new job to further reduce fuel consumption. Implementing these route optimisation technologies can provide fuel consumption savings of up to 20%.
Eco driver reporting helps you to create a culture of safer and greener driver behaviour, by monitoring the performance of your drivers across a number of eco driving indicators, including speeding, harsh braking and idling. The result is an improvement in fuel-efficient driving and an associated reduction in fleet fuel consumption of up to 10%.
The green fleet dashboard allows you to monitor your efforts in improving fuel economy and reducing CO2 emissions. It supports idling reduction policies, providing real-time notifications for excessive idling events and a management dashboard that highlights idling trends and outliers. Actively managing excessive idling can easily result in savings of £116 per vehicle per year.
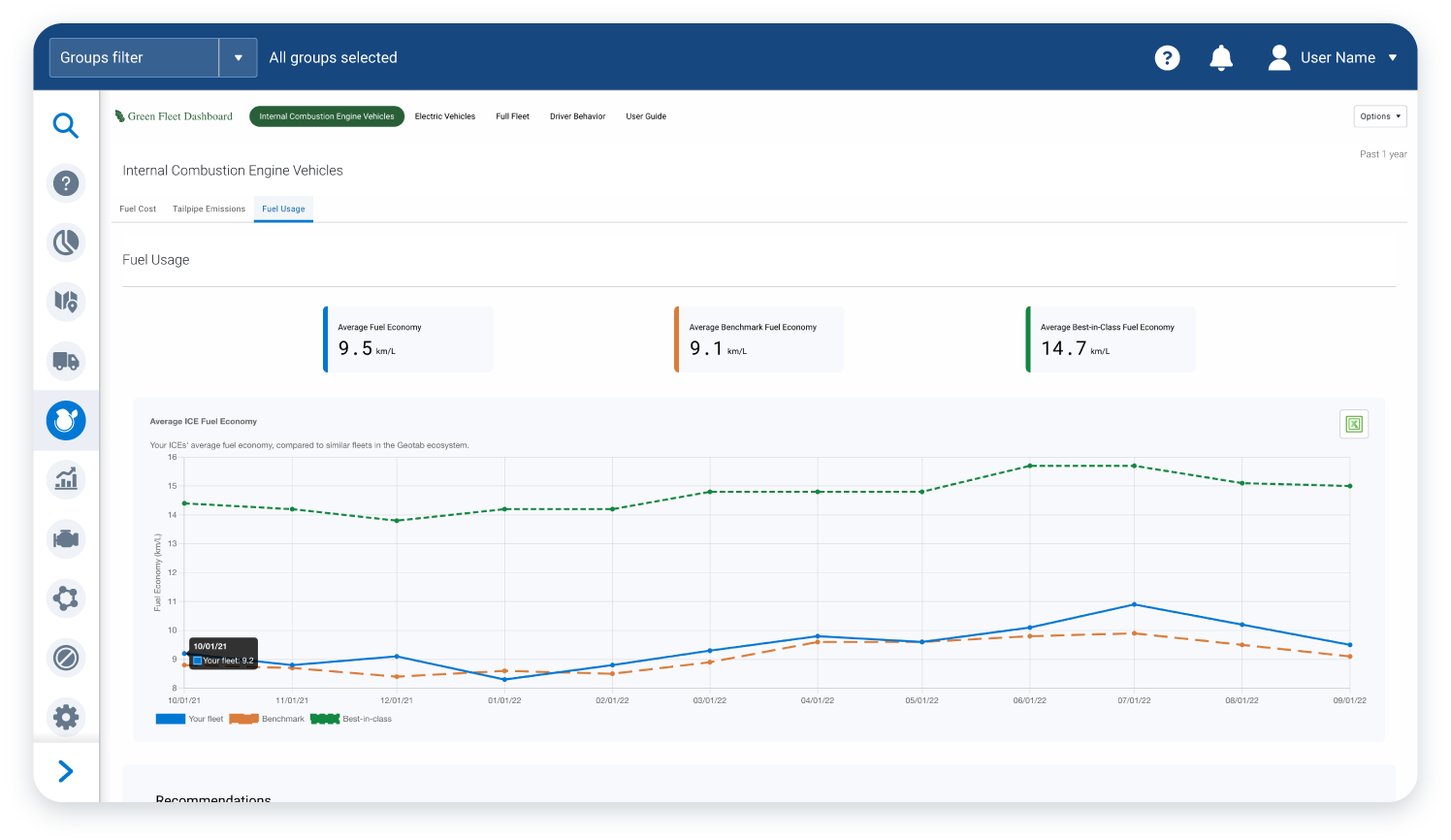
Green Fleet Dashboard - fuel economy report
Green Fleet Dashboard - CO2 emissions report
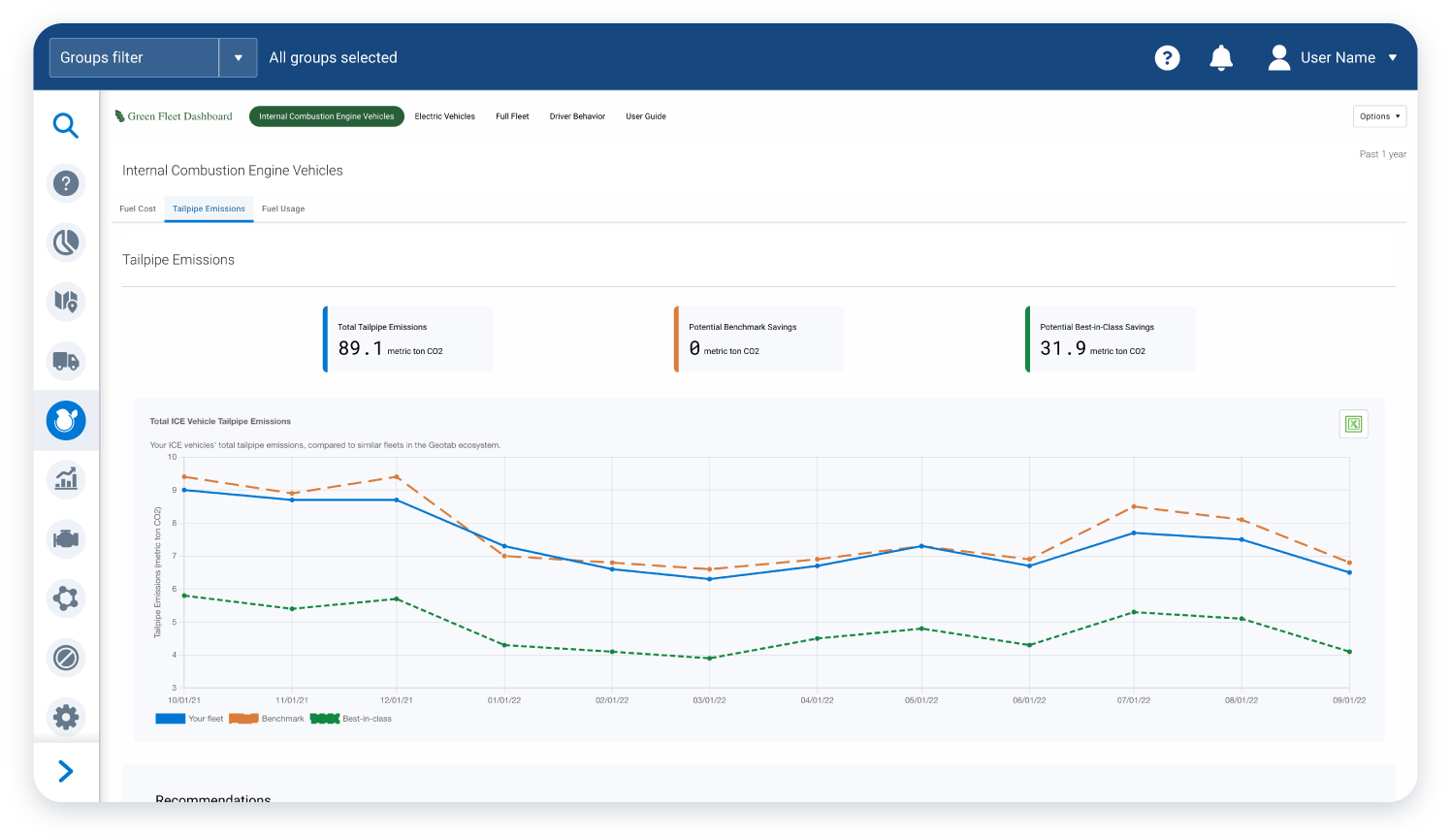
Active insights from real-time vehicle data can help to identify the vehicles that have the greatest environmental impact in order to prioritise optimisation strategies. With active insights, trials of technologies to improve fuel efficiency can be assessed in real time from a fuel economy and engine health perspective. Meanwhile, access to critical engine data for proactive vehicle maintenance can help to identify early engine faults, such as faulty oxygen sensors that would otherwise reduce fuel efficiency.
Transitioning to more efficient vehicles
Geotab’s electric vehicle suitability assessment (EVSA) supports the transition to electric vehicles, identifying the candidate vehicles for replacement and the electric models which would best fit the required duty cycles and offer the fastest return on investment. Analysis includes vehicle type, range capability and projected savings. One recent study has shown that transitioning to the right EV can amount to savings of £500 and 4 tonnes of CO2 emissions per vehicle per year.
See how Geotab’s EVSA helped Enterprise Fleet Management to uncover savings of millions of dollars, and hundreds of thousands of tonnes of CO2 emissions by transitioning to electric vehicles.
Case study - Geotab supports the decarbonisation objectives of DB Regio Bus
DB Regio Bus is the market leader in local transport throughout Germany. In its project with Geotab, one of the company’s core fields of action was to lower its CO2 emissions and therefore reduce energy costs for the company.
Almost all of the company's 5,000 owned buses were equipped with Geotab GO9 devices and the MyGeotab fleet management software provided immediate insights for the control centre, team management, fleet management, and maintenance departments.
In two years, DB Regio Bus substantially reduced fuel costs and leveraged data insights to optimise its fleet. Idling times were reduced by 40% in one year, reducing CO2 emissions by 1,400 tonnes per annum.
The driving style of individual drivers has been improved in a targeted manner by using telematics data, contributing to significantly lower fuel consumption, fewer accidents and increased passenger comfort. The goal is to use this mechanism to reduce CO2 emissions by 15,000 tonnes annually.
View the case study to learn more.
Conclusion
While the initial drive to measure the fleet’s GHG emissions and implement a decarbonisation strategy may have come from elsewhere within the organisation, fleet managers can expect to find a number of benefits beyond a reduction in the fleet carbon footprint. Besides the direct reduction in fuel costs, many fleets also cite improved safety performance and lower maintenance costs. There is growing evidence that these same strategies result in a happier workforce and can improve driver retention.
With Geotab’s actionable insights, this journey is made simpler so that you are saved the effort of scouring through the data to find where the greatest emissions savings can be made.
Subscribe to the Geotab Blog

Associate Vice President, Sales and Business Development, UK & Ireland
Table of contents
Subscribe to the Geotab Blog
Related posts

Strategic Implementation of Telematics for Optimising Last-Mile Delivery Operations
April 1, 2025
2 minute read
.jpg)
Lead with Trust: How Geotab Helps Businesses Navigate CSRD Compliance
March 19, 2025
2 minute read

Data-Driven Innovations in Fleet Management: highlights from Geotab Mobility Connect 2024
November 28, 2024
3 minute read

2030 or 2035, the UK Needs Meaningful Action on EVs Now
September 6, 2024
2 minute read

Driving smarter: Insights from Geotab’s “Taking Charge” Report
August 8, 2024
2 minute read
-EN-Na-final-July24_Card-1x.jpg)
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating: GVWR for heavy loads and lorries
June 26, 2024
2 minute read
